The plant posses an array of pharmacologically active phytoconstituents and has been reported to contain anthocyanidins, catechins, phenolic acids, quinones, friedo-oleananes, triterpene quinone-methides, and related triterpenoids (celastroloids). In particular the plant contains sitosterol, pristimerin, mangiferin, gutta-percha, dulcitol, three catechins (-)-epicatechin, (-)-epigallocatechin, and (-)-4’-O-methylepigallocatechin), two catechin dimers, salacenonal, salaciquinone, and two novel quinonemethide triterpenoids (celastroloids), isoiguesterinol and 30-hydroxy pristimerin, iguesterin, and epi-kokoondiol. Salacinol and kotalanol have been identified from both the roots and stems of S. reticulata.
Out of the identified components mangiferin, salacinol and kotalanol are major constituents responsible for the biological activities of the plant.
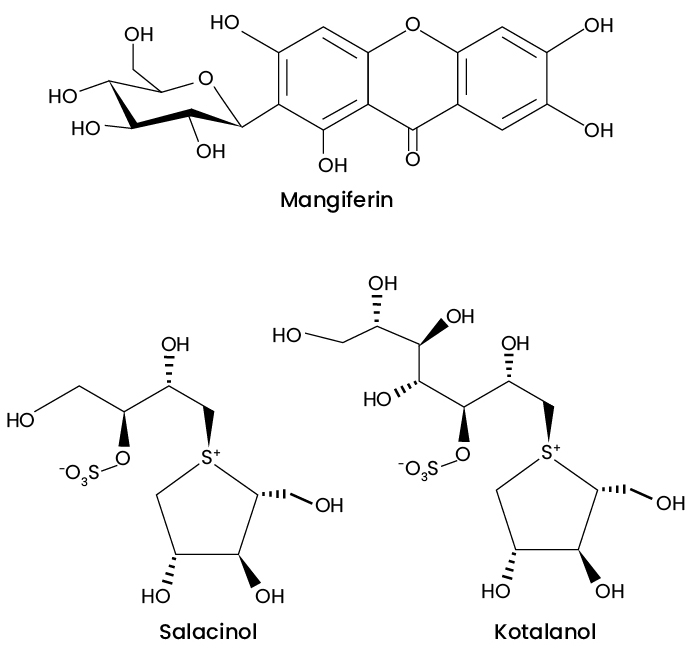
Reference
Arunakumara and Subasinghe S. Salacia reticulata wight: a review of botany, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Trop. Agric. Res. 2010;13(2):41-47.
