In a research study focusing on the effects of S. reticulata root extract, its potential to support healthy blood glucose levels was observed. This study involved both normal and model-induced conditions to explore natural variations in blood sugar management. The root bark extract of S. reticulata was administered over a period of 30 days. Observations from the study indicated that the extracts from the root and bark were effective in promoting healthy blood glucose levels in these conditions. Additionally, the extracts demonstrated significant antioxidant properties, suggesting a role in supporting overall cellular health.
Safety study
In a safety-focused study, Salacia reticulata extract was administered to mice at a dose of 2.3 mg/day for three weeks. The study aimed to observe any potential impact on various health indicators. Throughout the study period, there were no significant changes in body weight, fasting blood glucose levels, oral glucose tolerance, or liver enzyme activity (AST and ALT) between the control group and those receiving the extract. Additionally, key biological processes, including stress response, protein synthesis, transcription, cellular function, and metabolism, were not adversely affected, suggesting the extract’s safety profile. The study also noted that the extract supported the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels.
References
Im R, Mano H, Nakatani S, Shimizu J, Wada M. Safety evaluation of the aqueous extract Kothala himbutu (Salacia reticulata) stem in the hepatic gene expression profile of normal mice using DNA microarrays. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72(12):3075‐3083.
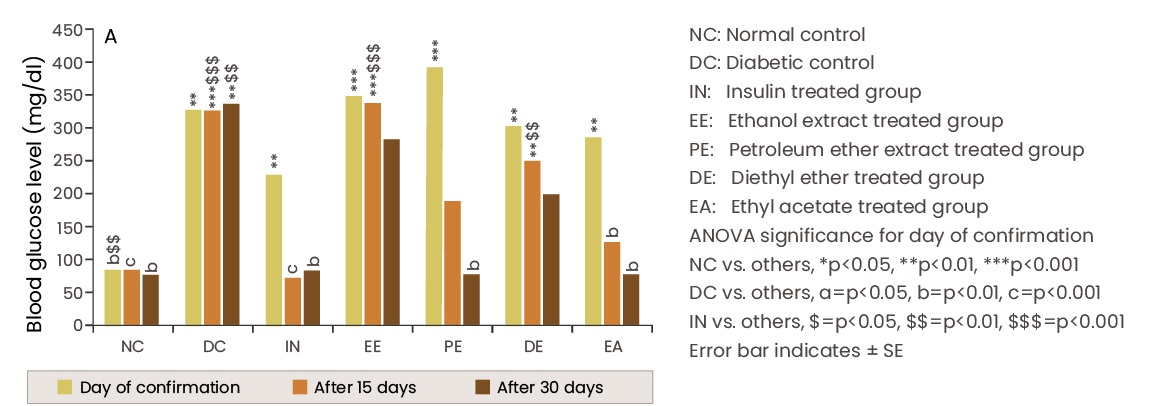
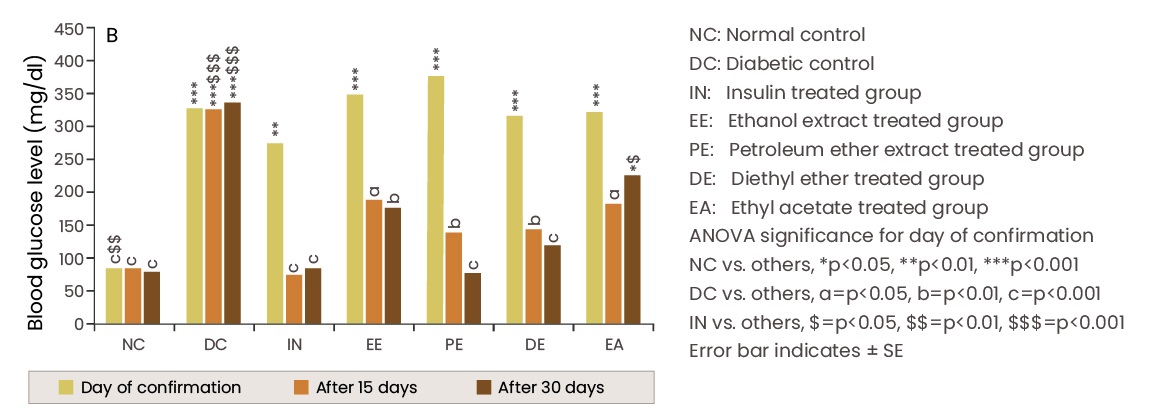
Chandrashekar CN et al., Free radical scavenging activities and antidiabetic properties of various extracts of Salacia reticulata. Thai Journal of Physiological Sciences. 2008;21(2):48-57.
